Juvenile Scoliosis
4-9 Years of Age
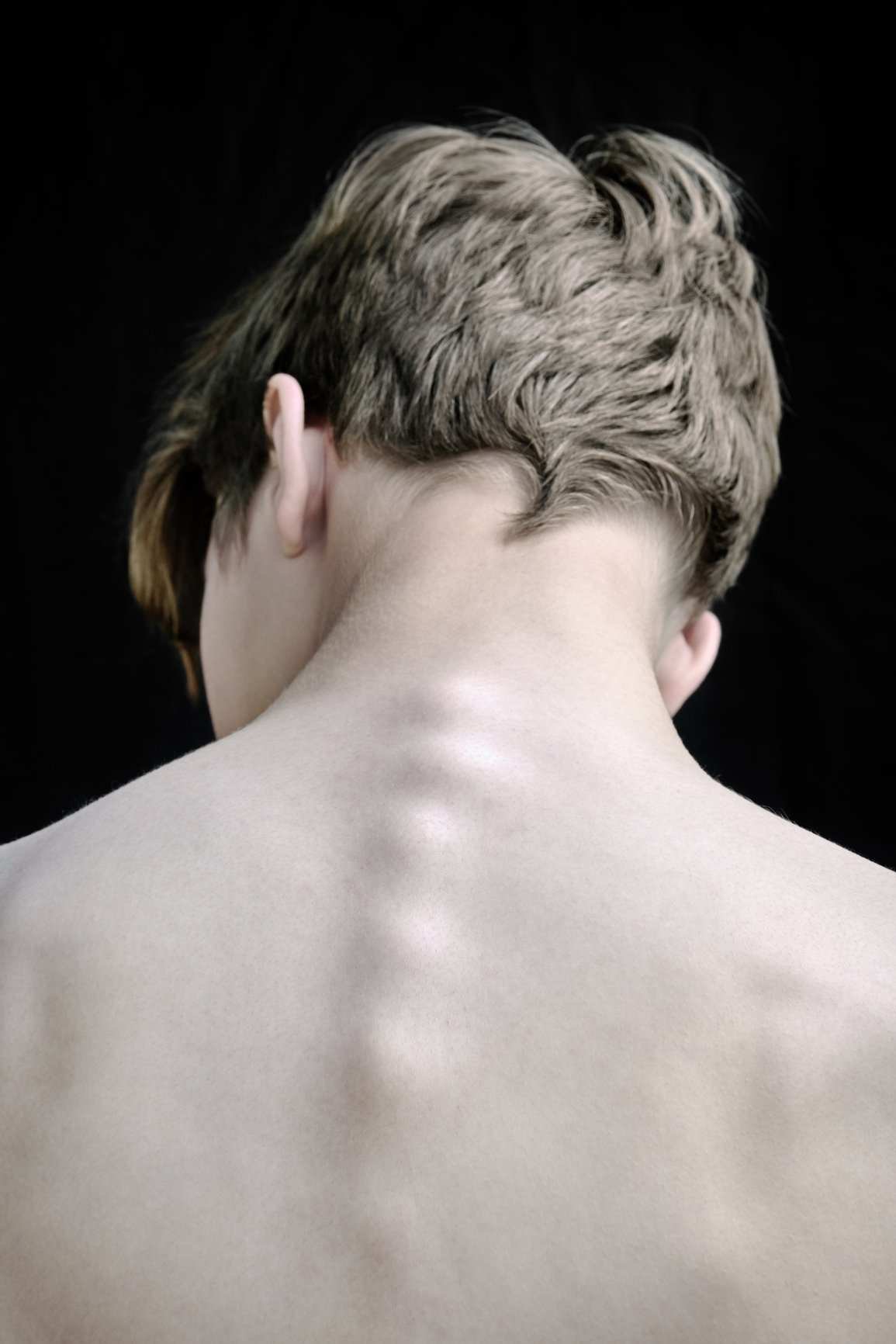
Juvenile scoliosis is an idiopathic scoliosis that affects children between the ages of 4 and 10. Like other types of scoliosis it is characterized by an abnormal sideways S or C curve of the spine.
Juvenile scoliosis is more often seen in girls than boys. In children between the ages of 4 to 6 years, the rate is fairly equal between the two sexes. However, between the ages of 6 to 10 years, the rate is much higher among girls. It is seen more frequently than infantile idiopathic scoliosis, but it is less common than adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.
Children with juvenile scoliosis generally have a high risk of progression of their curve. Seven out of ten children with this condition will worsen and require active treatment. Juvenile curves almost never resolve spontaneously. They usually require bracing.